Model Armor Evaluator
Introduction
As AI applications become increasingly integrated into business-critical systems, the need for robust security measures has never been more urgent. Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative AI systems face unique security challenges that traditional security tools cannot address. Google Cloud Model Armor emerges as a specialized solution designed to protect AI applications from malicious inputs, prevent sensitive data leakage, and ensure responsible AI practices.
This article explores Model Armor's comprehensive security framework, its critical role in LLM security, and provides practical insights into implementation and benefits through real-world application analysis.
The LLM Security Challenge
Modern AI Security Threats
AI systems face sophisticated attack vectors that exploit the unique characteristics of machine learning models:
Prompt Injection Attacks: Malicious actors craft special commands within text inputs to manipulate AI models, bypassing safety protocols and accessing unauthorized functionality.
Jailbreaking: Attempts to circumvent built-in ethical guidelines and safety measures, enabling models to generate harmful, unethical, or dangerous content.
Data Exfiltration: Prompts designed to extract sensitive information from training data or system prompts, potentially exposing intellectual property or personal data.
Content Manipulation: Exploitation of model behavior to generate inappropriate content that violates safety policies or regulatory compliance.
Traditional Security Limitations
Conventional security measures fall short in the AI context:
- Static Rule-Based Systems cannot adapt to the dynamic nature of language-based attacks
- Perimeter Security fails to address threats embedded within legitimate user interactions
- Post-Processing Filters may be too late to prevent harmful outputs from being generated
- Generic Content Filters lack the sophistication to understand context-dependent threats
Model Armor: A Comprehensive Defense System
Architecture Overview
Model Armor implements a dual-layer protection strategy that screens both inputs and outputs:
User Request → Model Armor (Input) → AI Model → Model Armor (Output) → Safe Response
This architecture ensures comprehensive coverage:
- Input Sanitization: Prompts are analyzed for malicious content before reaching the LLM
- Output Validation: Generated responses are screened for harmful or sensitive content
- Bidirectional Protection: Both layers work together to prevent attack vectors and data leakage
- Real-time Processing: Security checks occur without disrupting user experience
Core Security Components
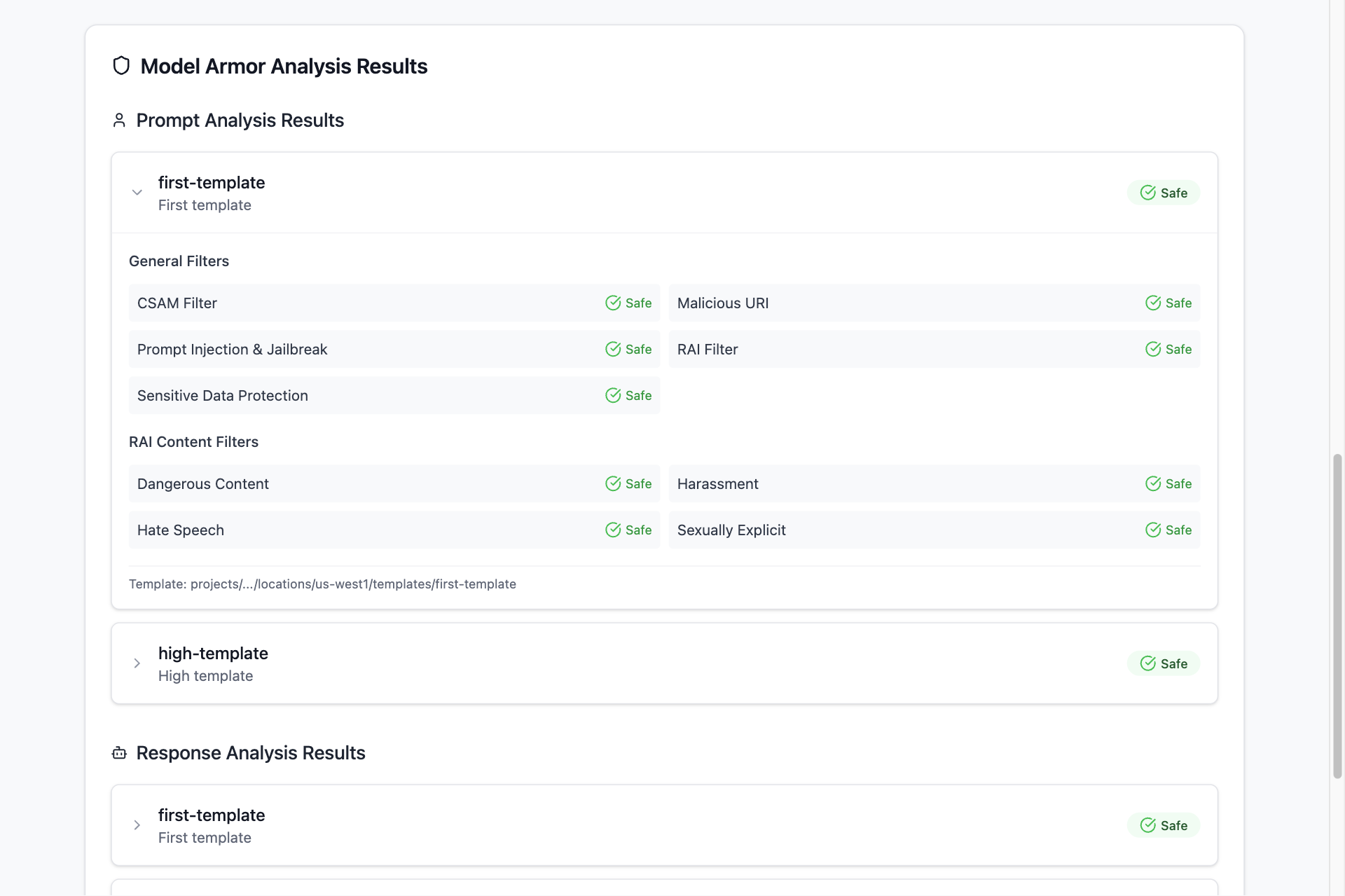
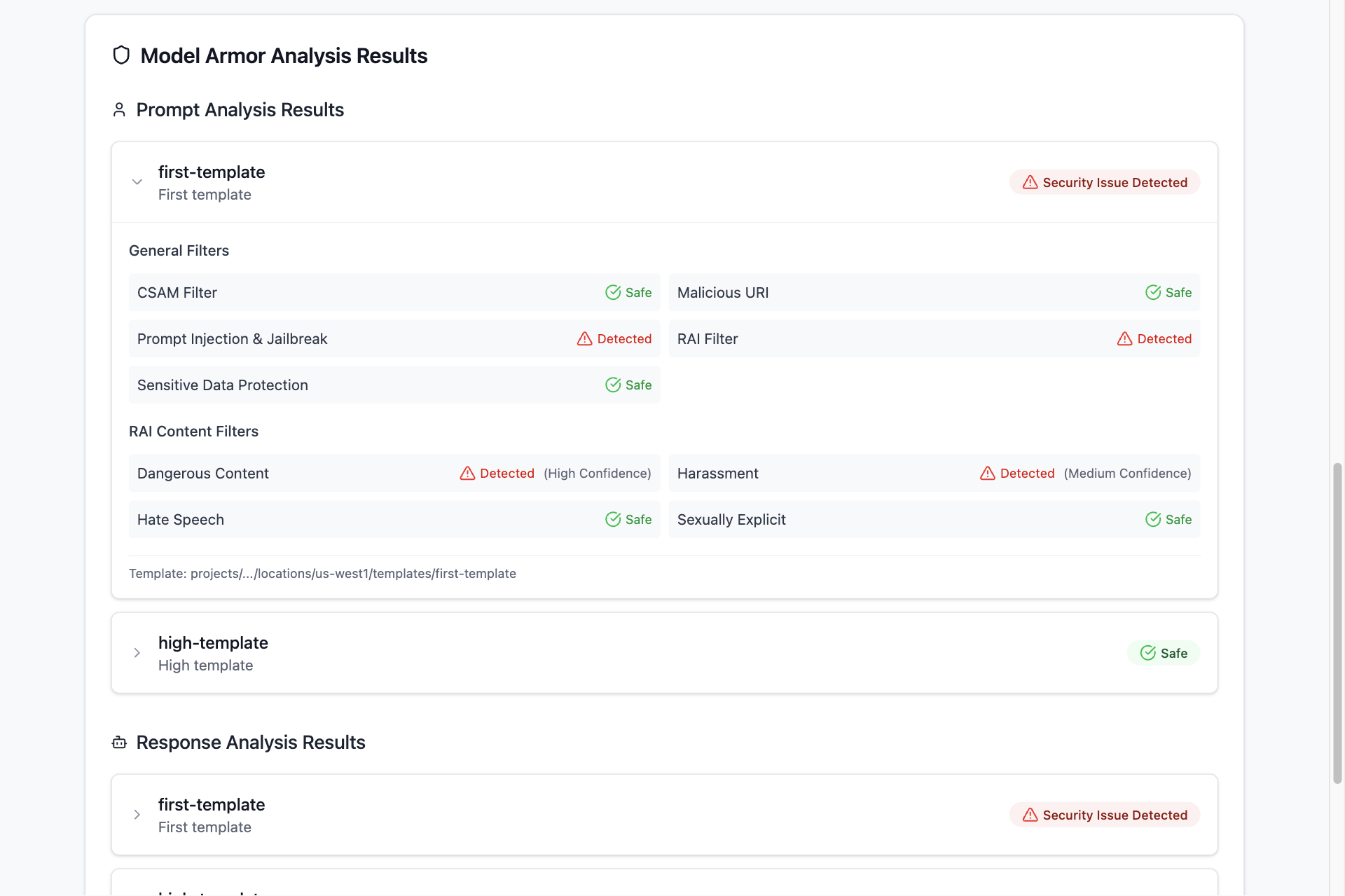
1. Responsible AI Safety Filters
Model Armor provides granular control over content safety across multiple categories:
- Hate Speech Detection: Identifies negative or harmful comments targeting identity and protected attributes
- Harassment Prevention: Detects threatening, intimidating, bullying, or abusive content
- Sexually Explicit Content: Screens for inappropriate sexual references and content
- Dangerous Content: Prevents promotion of harmful goods, services, and activities
Each category supports configurable confidence levels (High, Medium and Above, Low and Above) allowing organizations to fine-tune sensitivity based on their risk tolerance and use case requirements.
2. Advanced Threat Detection
Prompt Injection and Jailbreak Detection: Sophisticated algorithms identify malicious content designed to manipulate AI behavior. The system can detect subtle attempts to bypass safety protocols while minimizing false positives through confidence-based thresholds.
Malicious URL Detection: Automatically scans and identifies potentially harmful URLs that could be used for phishing attacks, malware distribution, or other cyber threats. The service processes up to 40 URLs per request for comprehensive protection.
3. Sensitive Data Protection Integration
Model Armor leverages Google Cloud's Sensitive Data Protection service to prevent accidental exposure of sensitive information:
Basic Configuration covers essential data types:
- Credit card numbers
- US Social Security Numbers (SSN)
- Financial account numbers
- Google Cloud credentials and API keys
- Tax identification numbers (ITIN)
Advanced Configuration provides:
- Custom inspection templates for specific business requirements
- De-identification capabilities that transform sensitive data while preserving context
- Industry-specific compliance support
- Cross-project template sharing with proper access controls
Multi-Language Support and Global Reach
Model Armor extends protection across linguistic boundaries:
Comprehensive Language Coverage: Tested and optimized for Chinese (Mandarin), English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, and Spanish, with broader language support available.
Flexible Activation Options:
- Per-request language detection for granular control
- Template-level configuration for consistent global protection
- Automatic language detection when source language is unspecified
Implementation: Model Armor Evaluator Case Study
To demonstrate practical Model Armor implementation, we analyzed a gRPC + frontend service that evaluates and showcases Model Armor's capabilities. The service processes user prompts, interacts with an AI model, and applies Model Armor's sanitization features.
Service Architecture
The Model Armor Evaluator implements a layered architecture that demonstrates secure AI application design:
type Handler struct {
templates *config.TemplatesConfig
modelArmorService *modelarmor.Service
genAIClient *genai.Client
}
Key Architectural Components:
- Configuration Layer (
internal/config/): Manages environment variables and template configurations - Service Layer (
internal/service/): Contains business logic for Model Armor integration and AI model interactions - Conversion Layer (
internal/converter/): Handles protobuf transformations between Google Cloud APIs and internal types - Server Layer (
internal/server/): HTTP/gRPC routing and static file serving
Security-First Request Processing
The service demonstrates secure request processing through its dual-sanitization approach:
func (h *Handler) Completions(ctx context.Context, req *connect.Request[pb.CompletionsRequest]) (*connect.Response[pb.CompletionsResponse], error) {
// 1. Sanitize user prompt before AI processing
sanitizationResult, err := h.modelArmorService.SanitizeUserPrompt(ctx, template.Name, req.Msg.Input)
// 2. Generate AI response using sanitized input
resp, err := h.genAIClient.Models.GenerateContent(ctx, req.Msg.Model, genai.Text(req.Msg.Input), nil)
// 3. Sanitize AI response before returning to user
modelSanitizationResult, err := h.modelArmorService.SanitizeModelResponse(ctx, template.Name, req.Msg.Input, resp.Text())
return response, nil
}
This implementation ensures:
- Pre-Processing Protection: Malicious inputs are detected before reaching the AI model
- Post-Processing Validation: AI outputs are screened for harmful or sensitive content
- Comprehensive Logging: Detailed sanitization results provide audit trails and monitoring capabilities
Template-Based Configuration Management
The service supports multiple security templates, allowing different protection levels for various use cases:
templates:
- name: "projects/my-project/locations/us-west1/templates/mid-template"
description: "Medium security template for general use"
- name: "projects/my-project/locations/us-west1/templates/high-template"
description: "High security template for sensitive applications"
This flexibility enables:
- Environment-Specific Security: Different protection levels for development, staging, and production
- Use Case Optimization: Tailored security policies for different application scenarios
- Compliance Requirements: Industry-specific templates for regulatory compliance
Getting Started: Implementation Guide
Prerequisites and Setup
Required Permissions:
- Model Armor Admin (
roles/modelarmor.admin) for template management - Model Armor User (
roles/modelarmor.user) for sanitization operations - Model Armor Viewer (
roles/modelarmor.viewer) for read access
API Enablement:
# Enable Model Armor API
gcloud services enable modelarmor.googleapis.com
Integration Best Practices
Client Initialization:
// Create location-specific client
opts := option.WithEndpoint(fmt.Sprintf("modelarmor.%s.rep.googleapis.com:443", location))
client, err := modelarmor.NewClient(ctx, opts)
// Implement proper error handling and connection management
service := &Service{
client: client,
location: location,
}
Request Processing:
// Sanitize input before AI processing
sanitizationResult, err := service.SanitizeUserPrompt(ctx, templateName, userInput)
if sanitizationResult.FilterMatchState == modelarmorpb.FilterMatchState_MATCH_FOUND {
// Handle detected threat appropriately
return handleThreatDetection(sanitizationResult)
}
Conclusion
Google Cloud Model Armor represents a significant advancement in AI security, addressing the unique challenges posed by modern LLM applications. By providing comprehensive protection against prompt injection, jailbreaking, sensitive data exposure, and content safety violations, Model Armor enables organizations to deploy AI systems confidently and responsibly.
The service's flexible architecture, multi-language support, and integration capabilities make it suitable for various deployment scenarios, from startup applications to enterprise-scale systems. Through template-based configuration and comprehensive monitoring, organizations can implement security policies that balance protection with functionality.
However, at present, Google Cloud Model Armor only accepts text input, and applying it to tool calling in modern AI agents requires additional effort on the user side. For example, when dealing with malicious file outputs or the execution of attack commands, it is important to note that additional implementations are necessary, and these countermeasures must be addressed accordingly.